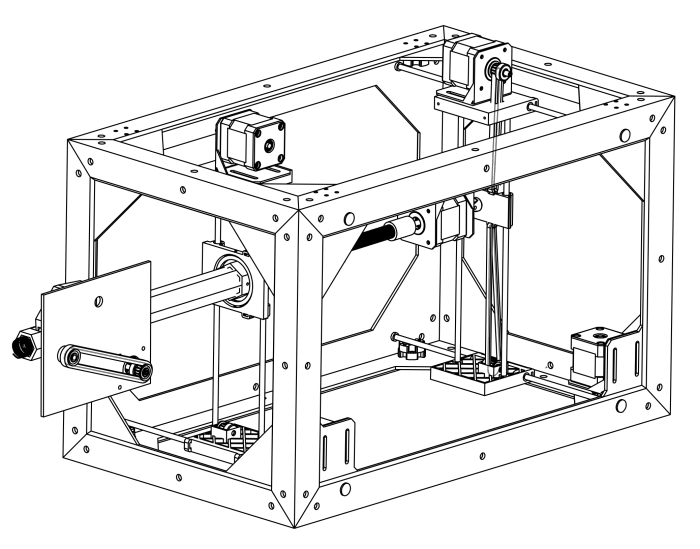

The design for this device was inspired by the MakerBot 3D printer. We simply made two two-axis positioning systems, offset them, and ran a rigid linear shaft between from one to the other. This defined the insertion line for the cochlear implant.
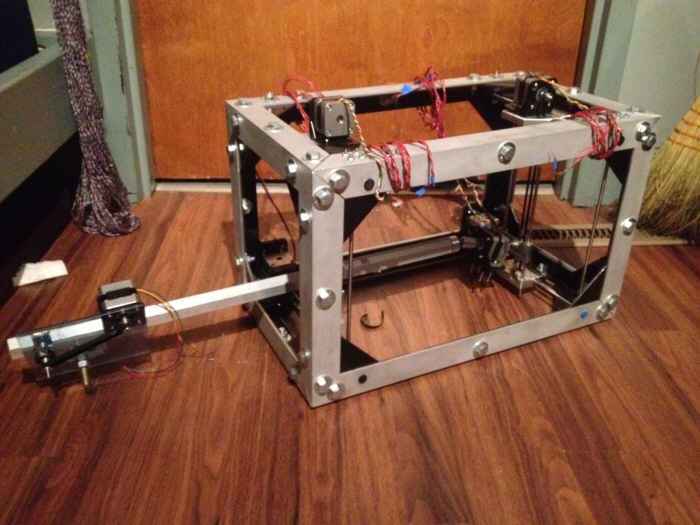
Not shown is the circuitboard and microcontroller, which provide the brains that allow us to move the device.
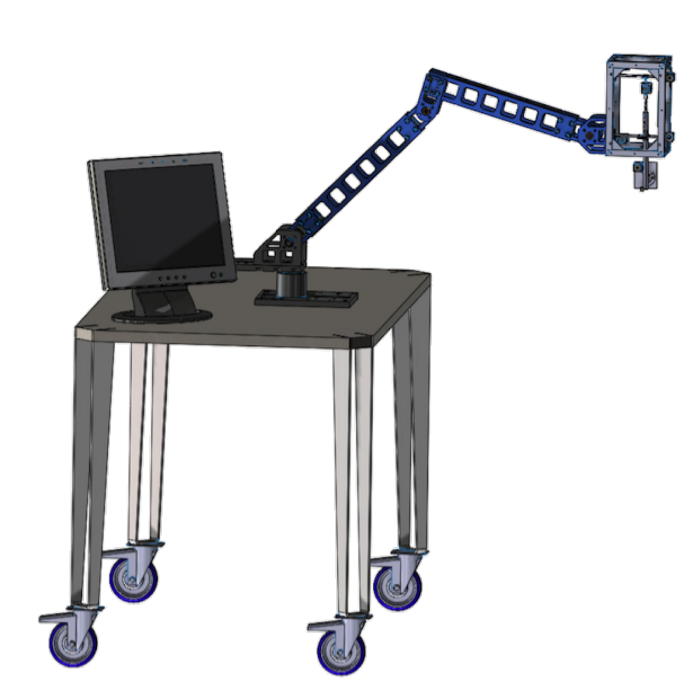

In the operating room, the device will be mounted on an arm with multiple degrees of freedom for coarse positioning. It will also incorporate a camera for improved visibility, which will be displayed on the monitor.
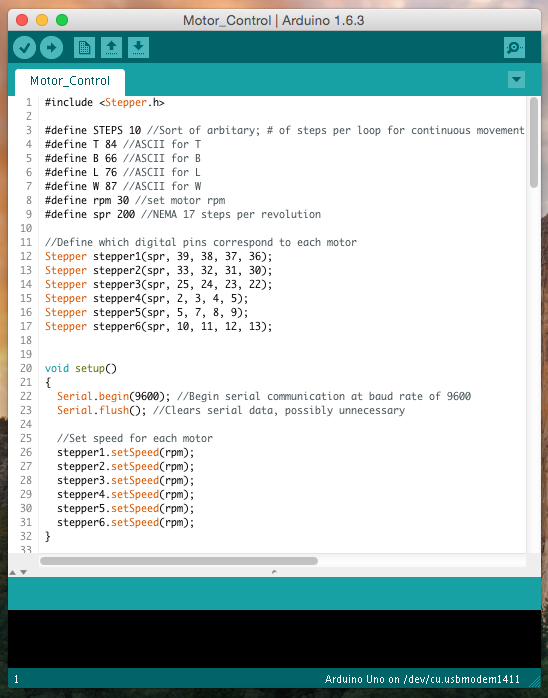
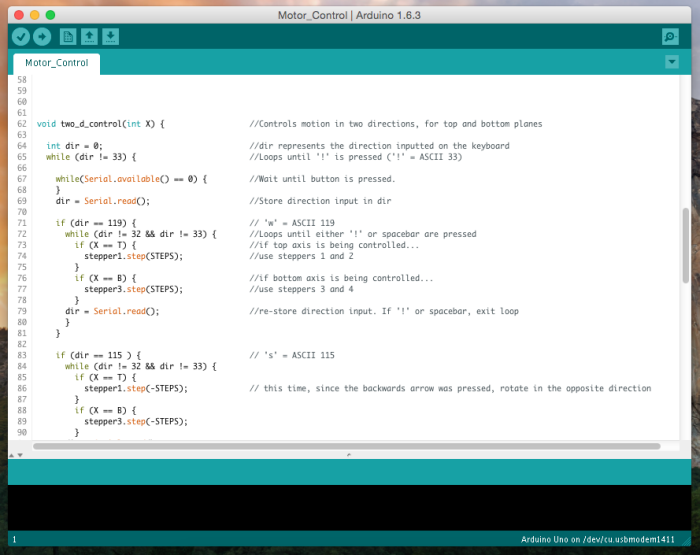
I wrote the code such that the back axis could be moved up and down, the front axis could be moved up and down, the shaft could be actuated forward and backward, and the insertion wheels (not shown) could be turned on to feed the cochlear implant into the cochlea.
gLike